Table of contents
Task 5 of #90daysofdevops
Write a bash script createDirectories.sh that when the script is executed with three given arguments (one is the directory name and second is the start number of directories and third is the end number of directories ) it creates a specified number of directories with a dynamic directory name.
Example 1: When the script is executed as
./createDirectories.sh day 1 90then it creates 90 directories as
day1 day2 day3 .... day90Example 2: When the script is executed as
./createDirectories.sh Movie 20 50then it creates 50 directories asMovie20 Movie21 Movie23 ...Movie50Answer:-
#!/bin/bash for (( i=$2;i<=$3;i++)) do mkdir $1:$i done lsWe just have to use 2 arguments while execution i.e.
./createDirectories.sh day 1 90./createDirectories.sh Movie 20 50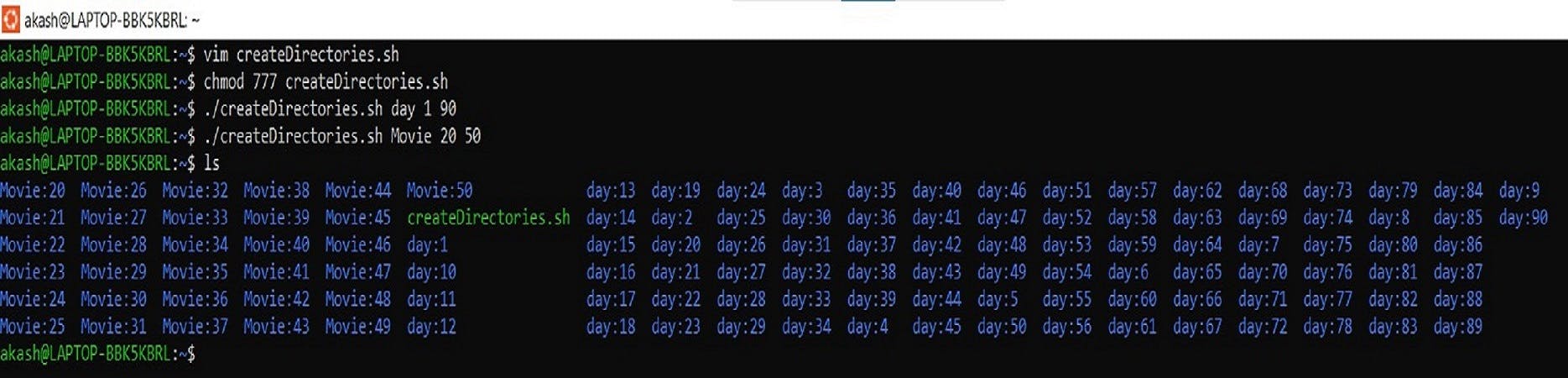
Create a Script to back up all your work done till now.
#!/bin/bash src_dir=/home/ubuntu/* dest_dir=/home/ubuntu/recovery curr_timestamp=$(date "+%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S") backup_file=$dest_dir/$curr_timestamp.tgz tar -cvzf $backup_file --absolute-names $src_dir echo "Backup is taken on $curr_timestamp" echo "Backup Completed successfully."About Cron and Crontab, to automate the backup Script
Cron
Cron is a service/process which allows scheduling or automating a particular task at a predefined interval.
Crontab
Crontab is a job scheduling utility used to schedule a particular script /Linux command written in a file for a specific time, day or period. It is configured in
/etc/crontab.crondis a daemon utilised to manage cronjob. Always used for regular tasks which helps in reducing human efforts & errors.Syntax:
crontab <option> <user>where options are
-e,-u,-l,-rTo create a new cronjob for the root user, use the following command and enter the new cron entry in a text editor
crontab -eTo list out the crontab list, use this command
crontab -lTo create a cronjob for the particular user, use this command
crontab -uTo remove created cronjob, use this command
crontab -rScheduling format :
* * * * * user-name <script/command path>1)Minute(0-59)
2)Hour (0-23)
3)Day of Month (1-31)
4)Month (1-12) or (Jan, Feb, Mar,......., Dec)
5)Week (0-7) or (Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun)
where,
* means all/unknown- means Range, means list/separator/ means intervalExample :
17 6 * * * echo "This is my first cron job" > /home/ubuntu/first_cronjob.txt
About User Management
A user is an entity, in a Linux operating system, that can manipulate files and perform several other operations. Each user is assigned an id that is unique for each user in the operating system.
id 0 is assigned to the root user and the id's 1 to 999 (both inclusive) are assigned to the system users hence the ids for local user begins from 1000 onwards. In a single directory, we can create 60,000 users.
Command to list all the users:
awk -F':' '{print $1}' /etc/passwdwith the help of the awk command, we are printing the first column separated by “:”
Command to get the id of a user:
id usernameCommand to add a user:
sudo useradd usernameCommand to assign a password to a user:
passwd usernameCommand to access user configuration:
cat /etc/passwdCommand to change userid:
usermod -u new_id usernameCommand to modify the group id of a user:
usermod -g new_group_id usernameCommand to change login name for a user:
usermod -l new_login_name old_login_nameCommand to change the home directory of a user:
usermod -d new_home_dir usernameCommand to delete a user:
userdel -r usernameNote: If a user is part of a group, then we have to remove the user from the group and then delete the user.
Create 2 users and just display their Usernames
sudo useradd Shawnsudo useradd MendisTo display their usernames, the following command is used:
awk -F':' '{print $1}' /etc/passwd
Reference link: https://youtu.be/aolKiws4Joc
Thanks for reading.
See you next time.
